Everything about gas cylinders
Last Updated on 1 year by Lajos SZABÓWe collected all information about gas cylinder production, parts, certifications, accessories and everything what is connected to this topic. We hope you will find what you are looking for.
What is a gas cylinder? (definition)
On technical field when we would like to specify something in an exact way then we always have to go back the the basics – to the standards on gas field. The most basic standard would be the ISO 10286 Gas cylinder – terminology. It contains everything connected to the gas cylinder but unfortunately not the “gas cylinder” itself.
In general when we are talking about gas cylinder (or gas bottles) then we talk about a gas container between 0,5 liter and 150 liter. The purpose is to store gases or liquified gases above atmospheric pressure. Therer are limits in this definition: If the container is smaller then 0,5 liter then we call cartridge, patroon. If it is bigger than 150 liter then we regularly call tank, bundle, MEGC, vessel, container…
The gas cylinder is useless. Everybody want to use the gas inside and not the gas cylinder. The gas cylinder is only a packaging.
Gas cylinder

Gas cylinder types
Gas cylinder product groups
STEEL gas bottles
The most standard and cheapest solution for gas storage. That is why mostly you will find 34CrMo4 Chrome molybdene specification on most of the steel cylinder drawing. Low cost for raw material with higher production energy.
ALUMINIUM gas cylinder
clean solution without corrosion. Optimal for food or medical industry. The aluminium is netural for magnetic, that is why you can use it in an application like MRI. Well known aluminium alloys for gas cylinders are AA6061, AA7032, AA7060, AA2001. The high value special gas mixtures or high purity gases will keep their quality for longer time than in a steel cylinder. The advanced aluminium materials could save weight against the steel cylinders.
STAINLESS STEEL gas cylinder
Rather high priced solution for gas storage. Very rare in usage and in production as well. If the gas is very very agressive or cost for a billion then this could be an optimal choice.
PLASTIC gas bottles
In this pressure range what we are talking now regularly the “only plastic” solution is not presented. The plastic cylinder base liner regularly could part of a composite cylinder -see later.
COMPOSITE bottle
Liner
The composite cylinder is produced from combination of more materials. Regularly there is a base form (called “liner”) what give the shape f the cylinder and give the stable surface to apply the pressure bear elements. The liner itself would be able to keep only max 60 bar but with different fiber wrappings the working pressure is increased to 200 bar, 300 bar, 500 bar or more!
Structure
The most common 3 layer in a composite cylinder is the liner, then the pressure holding wrapping like carbon fibre or glass fibre. Then some case a protection wrapping is applied as well. For example on the breathing apparats cylinders you can see the black/grey carbon fibre wrapping and over it there are some light coloured/white glass fibre wrapping to protect the carbon fibre. There are many type of composite cylinders which vary the liner material (steel, aluminium, plastic or carbon) and the wrapping material (glass or carbon fiber). The variation could come from the position of the wrapping as well like only wrapping on the hoop or wrapping all over (full wrap cylinder).
Pressure ranges
- Low pressure gas cylinder – low pressure bottles maximum working pressure is regularly 35 bar (500 psi)
- High pressure gas cylinder – everything above 35 bar we refer to them as a high pressure cylinder
The working pressure and test pressure is a basic obligatory data on a gas cylinders’ neck. In case you need lower pressure at the user side then you can always use a pressure regulator
The basic form of the raw material to the gas cylinder production could be:
Base material for production
- From Plate – regularly here we deep drawn the plate to the necessary form. And from 2 or 3 pieces we weld together the cylinders,
- From Billet – from a metal block called billet (it is a solid metal cylinder) after heating you form the shape of the body of the gas cylinders. Here you form together the body/hoop and the bottom. The neck form will be created later with hot spinning. Some more information and goods could be found on engineering gallery: Hot Piercing or Seamless tubing | Engineers Gallery
- From Tube – when the proper tube cutted into the desired length and then the neck and bottom form is produced with hot spinning technology.
Transportability
- Transportable – most of the cylinders could be transported with pressure like cylinders approved under TPED (transportable pressure equipment directive 2010/35/EU). The standard usage of these gas bottles are: the gas factory filled the cylinder then transport to the user’s location. After the user used the gas for welding or for medical treatment for example the cylinders are transported back to the filling place.
- Stationary – there are approval process where not the transportation is the main issue but the dynamically changing pressure is the hardest part. This could be a PED ( pressure equipment directive 97/23/EC and 2014/68/EU). The typical usage of these cylinders are for example beside a compressor station or at a CNG filling station.
Type of gas cylinders
- Type 1 (T1) – all metal cylinder
- Type 2 (T2) – metal liner + wrapping on the hoop
- Type 3 (T3) – metal liner + all over fiber wrapping
- Type 4 (T4) – plastic liner + all over fiber wrapping
- Type 5 (T5) – only carboon material (the liner and the wrapping as well)
Gas bottle filling frequency
- Refillable – when the cylinder is filled many many times during its lifetime. Typically these cylinders will be filled daily or on a weekly basis without any problem. You have to make the necessary maintenance on a deifnite period.
- Disposable – the cylinders are degined and produced for only 1 time filling and using. Typical cylinder of these are for example soda patroon or N2O (dinitrogen-oxyd) cartridges for foam production.
Filling material
- For permanent gases – typical application is an oxygen or nitrogen cylinders. Here the gas will remain in gas state during the all filling process. The bottle will have working pressure and testing pressure as well. The cylinder material has to be in line with the gas compatibility (ISO 11114) . If
- For liquified gases – the cylinders are produced for gases what under pressure transform into a liquid form. Regularly here the cylinder’s data only contains a test pressure but not a working pressure.
- For dissolved gases – there are gases – typically acetylene – what would be dangerous for transport with the same condition like other permanent gases. The gas itself would be so unstable that it would cause an explosion. That is why the acetylene is dissolved into other material where the transportatino on low pressure could be much more safer.
Type of gas cylinders
 Production of gas bottles
Production of gas bottles
Method for gas cylinder production
There are 3 main production mode of the gas cylinders (now I am talking only metal type one gas cylinder production). The most simple production production process is to form the neck and the bottom of the gas cylinder on a press with deep drawing. These parts are mainly formed from a plate. Then weld those parts together with the following methods:
- If you weld only the upper part to the bottom part then you will produce a cylinder from 2 piece
- If you weld the neck and the bottom part to a the hoop (middle body) then you will produce the cylinder from 3 piece. The hoop could be produced from a tube with cutting or could be produced from a plate with rolling and welding.
The second big group of production when you product the bottle without any seam. This we called seamless. For the base material at seamless cylinders could be 2 option:
- Produce from tube
- Produce from billet with piercing and hot spinning neck forming
Gas cylinder production standards
We listed the technical details of the gas bottles production. The design and the approval process is a different issue. There are plenty of gas cylinders connected to the gas industries. Different standard regulate the productio of aluminium and steel or composite cylinders. Low pressure and high pressure is also a different issue. The most well known standards are:
Most common gas cylinder design and production standards
- EN I1964-3 – Transportable gas cylinders. Specification for the design and construction of refillable transportable seamless steel gas cylinders of water capacities capacity from 0,5 litre up to 150 litre
- ISO 9809-1: Gas Cylinders–Refillable Seamless Steel Gas Cylinders–Design, Construction and Testing–Part 1: Quenched and Tempered Steel Cylinders with Tensile Strength less than 1 100 Mpa
- ISO 9809-2: Gas Cylinders–Refillable Seamless Steel Gas Cylinders–Design, Construction and Testing–Part 2: Quenched and Tempered Steel Cylinders with Tensile Strength Greater than or Equal to 1 100 Mpa
- ISO 9809-3: Gas Cylinders–Refillable Seamless Steel Gas Cylinders–Design, Construction and Testing–Part 3: Normalized Steel Cylinders
- EN ISO 11120 – Gas cylinders. Refillable seamless steel tubes of water capacity between 150 l and 3000 l. Design, construction and testing (ISO 11120:2015)
- EN 1975 – Transportable gas cylinders. Specification for the design and construction of refillable transportable seamless aluminium and aluminium alloy gas cylinders of capacity from 0,5 litre up to 150 litre
- EN 84/526/EEC – Aluminium high pressure gas cylinder deisgn
- EN 12245 – Transportable gas cylinders Fully wrapped composite cylinders
- ISO 11119-1 Gas cylinders — Design, construction and testing of refillable composite gas cylinders and tubes — Part 1: Hoop wrapped fibre reinforced composite gas cylinders and tubes up to 450 l
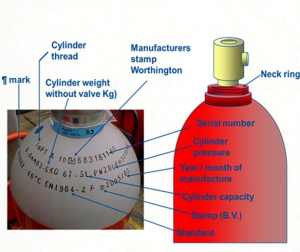
Producer signs on the gas bottles
We are working on high pressure dangerous field. Of course the identification is very important. We have to be able to always trace back the every gas cylinder to its producer. All marking on gas cylinder neck include of course the identification of the gas cylinder producer as well. 3 main sign cover the identification needs:
- Produced identification stamp
- Production date
- Serial number of the gas cylinder
Approval process of gas cylinders
 Beside the phisicyal production of the gas cylinders there are plenty of certification documentation and approval process for special areas. In Europe the most common gas bottles certifications are:
Beside the phisicyal production of the gas cylinders there are plenty of certification documentation and approval process for special areas. In Europe the most common gas bottles certifications are:
- TPED (transportable pressure equipment directive) – gas cylinders what could be delivered with pressure inside
- PED (pressure equipment directive) – mainly stationary equipment part of a pressure holding/processing system. But in this certification area you can find the SCBA (self containing breathing apparate cylinders) or the fire extinguisher CO2 cylinders or scuba (diving) as well
- ECER110 – gas cylinders for fuel of vehicles
In US the standard is the DOT (Department of Transportation).
These standards regulate the design, testing type approval and certification processes, marking requirements for the pressure equipments.
Gas cylinder identifications
The safety marks of a gas cylinder contains different elements. All stamp, color coding, stickers are a complete system. You can see not easily modifiable marks like stamping on the gas cylinder neck. You see well recognisable marks from the distance. It could be the colour of the cylinder. Or you have temporary stickers what show you the actual last filling and filler of the gas cylinder.
- The stamped marks on the gas cylinder neck and the bottom give you a lifelong signs what is connected to the gas cylinder tracebility. Regularly it won’t change during the lifetime of the gas cylinder. Producer, production year. Country of production, standards of the production/certification. Gas type if any specific. Weight of the gas cylinder…all information what is strictly bind to the construction of the gas cylinder.
- Color codes give a good recognition form distance for the content of the gas cylinders. As a general rule the body color give you the use of area (white- medical, green- special gas, yellow-food, grey-industry). The neck color in an obligatory way give you info on the type of gas inside (red-flamable, yellow-toxic,…)
- Stickers – give you a trace back to the last filling place, gas producer. Give you the ADR data what is obligatory.
Part of the gas cylinders
The main parts of the gas cylinders are: foot, neck ,hoop (body). Some parts could be attached to the gas cylinder like neck ring or welded cages. You can have a detailed description on all part what containes the foto type for example like concave or convex foot.
Size and dimensions of gas cylinders
What are the main standard sizes of the gas cylinders. 2 kg 5 kg 10 kg CO2 cylinder you can always hear from users or from gas factories, You can put short CO2 under the counter if you are a bartender. You regularly transport 50 liter O2 or acetylene cylinder if you make welding jobs on site. Firemen already have action with 6,8 liter composite cylinder on back in hot situation. Medical workers in hospital or in an ambulance care use 2 liter, 5 liter, 10 liter, 20 liter. We collected all standard size of the gas cylinders. We explain why we call cylinders with liter, with m3 or with kg.
There are very important situation when you have to know what are the exact dimensions of the gas cylinders. You have limited space to store or to use the gas cylinder. This could be a water dispenser machine where you put a CO2 cylinder. Maybe there is a limited space in the ambulance car for the oxygen cylinder. Length, diameter with accessories or without accessories. What is the approximate weight of a gas cylinder?
- Gas cylinder sizes – list and short explanation on main sizes (liter, kg, m3)
- Gas cylinder dimensions – main parameters of the gas cylinder (length, diameter, dimensions with accessories…)
Accessories for gas cylinders
When we use a gas cylinder we use many other accessory with it. If we just think on the valve. Without a valve it would be difficult to keep any gas inside the cylinder.
- Gas cylinder valve
- Pressure regulator
- Valve protection cap
- Protection cage
- Protection plastic net.
- Metal pallets
Beside these several example we give you a complete guide on accessories for gas cylinders.
Storage and transportation of gas cylinders
In Europe the ADR („Accord européen relatif au transport international des marchandises dangereuses par route“) regulate the safe storage and
Lifetime of a gas cylinder and scrapping of gas cylinders
In general the standard gas cylinder do not have a definite lifetime. We could say if the cylinder passed on the testing process without problem then it coudl stay in service. This rule could be different in several country or in several gas cylinder design and testing standard. For example there was time when in Hungary the old cylinders produced by “Csepel Csőgyár” lifetime was max 50 year. It was changed later.
When gas cylinder composite cylinders start to be standard solutions then based on the cycle tests and based on the results the first gas cylinders receive a maximum lifetime of 15 years. After the years past there was no any possibility to keep the cylinders in life. Even if a SCBA composite cylinder dusted on a shelf at a fire brigade without any use that has to be scrapped.
Later in the composite cylinders more type arrived with 20 year lifetime then 30 year lifetime then with unlimited lifetime.
When a gas cylinder lifetime passed or the cylinder failed on the periodic inspection then the gas cylinder has to modify to be able to impossible to fill it – or repair it to another fill. You have to damage with cut or flame the thread and make holes on the neck and on the body.
Maintenance of gas cylinder
In general the international standards require – at a normal gas cylinder – to go for testing every 10 year. The period could be shorter in case of aggressive and corrosive gases. like Chlorine or sulphur dioxide. The ADR define exactly the time period of the inspection time.
There are special areas which regulate their own periods. The most common areas are:
- Fire extinguisher’s cylinder
- Cylinders for vehicles
- Scuba or SCBA cylinders
- Country by country could be different local regulation
A maintenance process contains many steps. Identify the cylinders evaluate the inner and outer state of the gas cylinder. Check the corrosions on it. Make a pressure testing on 1,5 times higher pressure then the working pressure.
Transportation of gas cylinders
During transportation or only at gas plant storage you have to secure the gas cylinder against falling. The ADR give you a full guidance on gas cylinder handling. This could be a chain fixed to the wall or a cylinder transportation metal pallet what provide the secure strapping of the cylinders and a secure forklift pockets and lifting eyes for crane.
During transport or storage you always have to keep on the valve protection cap or cage. This could avoid the accident if the cylinder would fall because of any cases.