Gas cylinder bundle usage
We summarise the information connected to gas cylinder bundle (or gas packs or gas battery) what you should know for your best choice.
Definition of a gas cylinder bundle
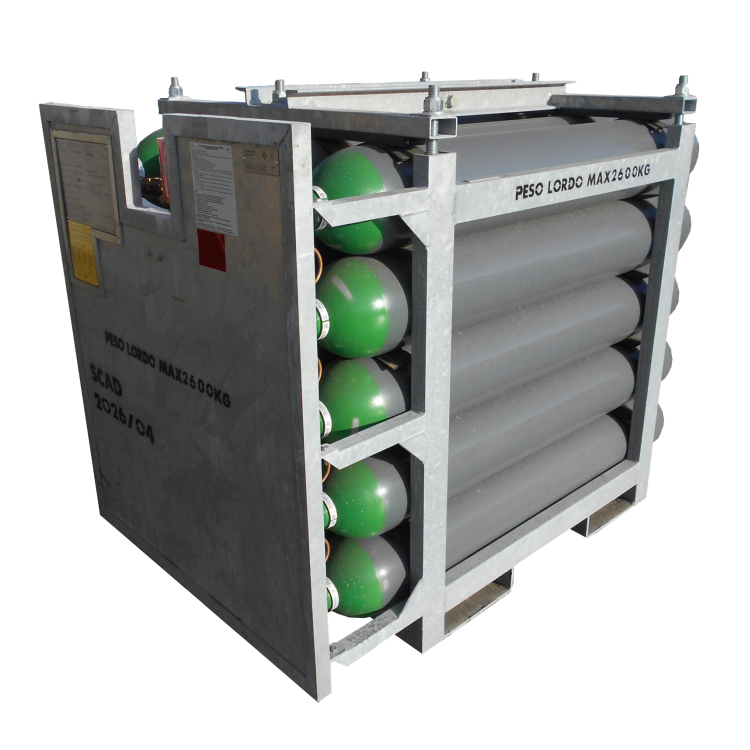
Portable assembly which consists of a frame and two or more cylinders, each of the capacity up to 150 liter and with combined capacity of not more than 3000 liter or 1000 liter in the case of toxic gases, connected to manifold by cylinders valves or fittings such the cylinders are filled, transported and emptied without disassembly (ISO 10961). As an exaple you can see our product range.
Who is not familiar with the gas industrial area regularly could mix the gas cylinder bundle and the gas cylinder pallets.
- The bundle is filled together and used together. It is only dismounted when it is tested (every 10 year in general)
- The pallet hold single cylinders during storage and transportation. It make easier the handling, but the cylinders are filled and used separately.
How could we name the gas cylinder bundle on other name?
In different countries you can name the gas cylinder bundle for example:
- Gas battery
- Gas pack
- Gas bundel
- Gas quad
Why do we use a gas bundle?
There are cases when we need more gas than a content of a single cylinder (10-15 m3). For example we would use higher quantity of gas at a laser cutting machine. We should change the nitrogen gas cylinder every hour or more frequent. In this case we have to find some other solution for bigger quantity of gas. If the gas usage is huge and constant then of course we could install a cryogenic tank (3-20 Nm3 liquid) into the plant. If the gas usage is between a cylinder and a cryogenic use or the use is temporary or because of any other objective reason against the cryogenic tank installation then the gas bundle is a good solution. You will fill and use 12 or 16 or more gas cylinder together through the main valve. You do not have to change cylinder by cylinder your gas source.
Some other example of use of gas cylinder bundles
- Beside compressors or PSA generator as a high pressure buffer
- In a university for experimental
- Industrial scuba diving
- Rocket science and space research for helium transport and use
- Stationary air reserve for a chemical plants for SCBA breathing protection
- Gas factory gas transportation
- etc.
When you should not install a cryogenic tank?
- NOT ENOUGH GAS USAGE: You do not have enough gas usage (minimum capacity of a installed Cryo tank is 3 m3) – Can you use that gas in a 2-4 weeks?
- LOSS ON WARM UP: The cryogenic tanks has a great insulation. In spite of this good insulation the gas inside the cryo tank is getting warmer and warmer. If you do not use the gas continuously the pressure will reach the level when the safety valve will release the overpressure – this will ba a loss for you.
- HIGH RENTAL fee or INVESTMENT The cryogenic tank – if it is owned by the gas factory – is a bigger investment and a longer contract with renting fee
- ONLY IN INDUSTRIAL AREA: The place is not good for install a cryogenic tank – for example it is not a massive industrial area
What is the size limit for a gas cylinder bundle?
As it is arriving from the definition we have 2 limit:
- The single cylinder cannot exceed the 150 liter water capacity.
- The total water capacity of a gas pack has to be under 3000 liter (or 1000 liter in case of toxic gases)
So for example you can have 60×50 liter gas cylinder bundle or 20×150 liter bundle as well. They are not really common. The most standard bundles what is widely spreaded in the industry is the 12×50 liter or the 16×50 liter.
Above these limits we called MEGC (multi-element-gas-container) or ISO gas container.
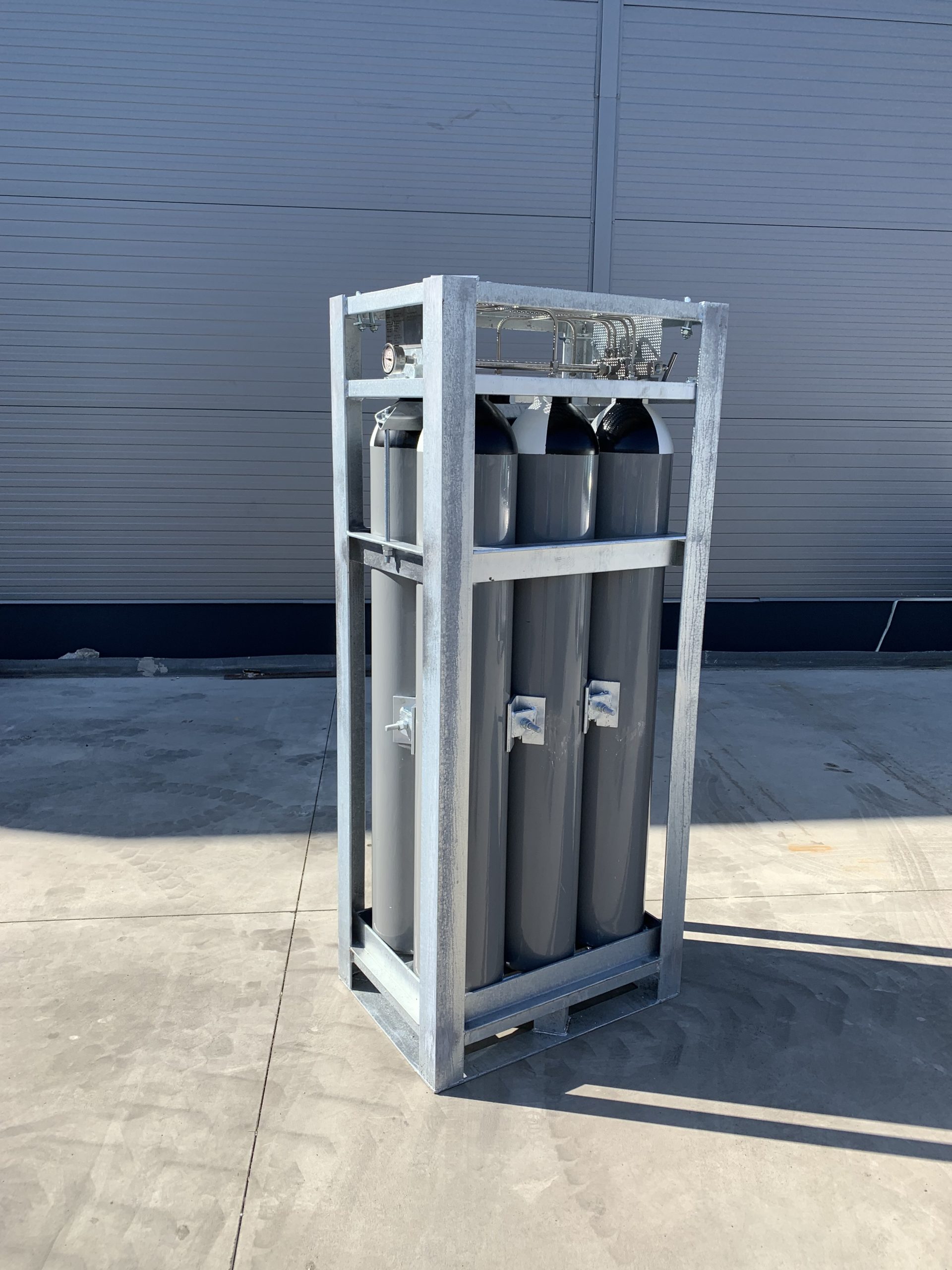
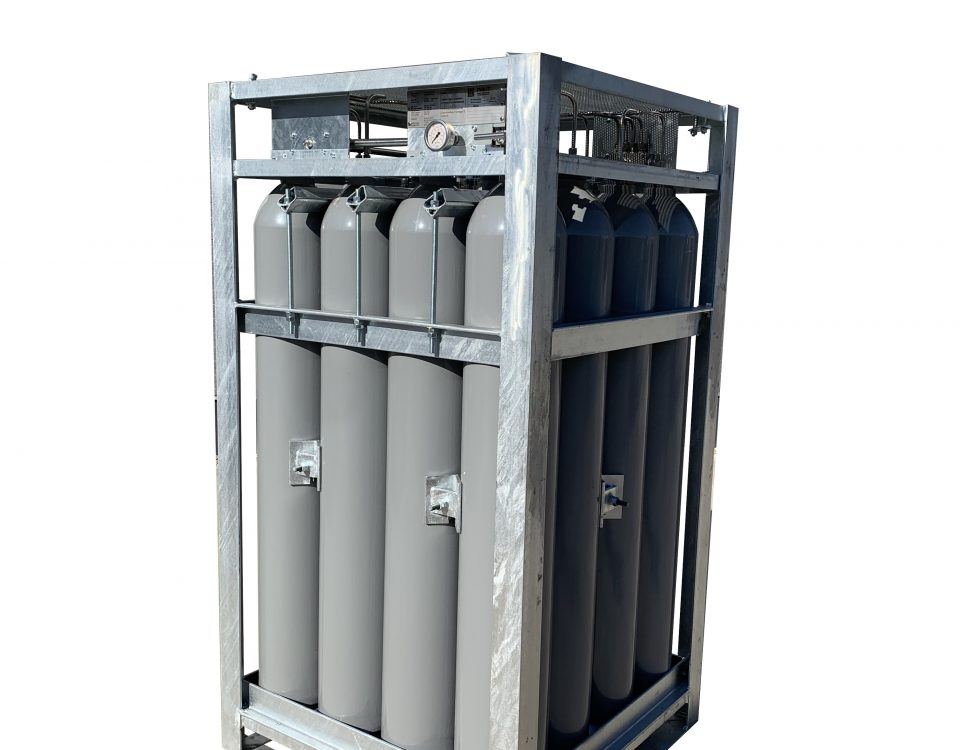
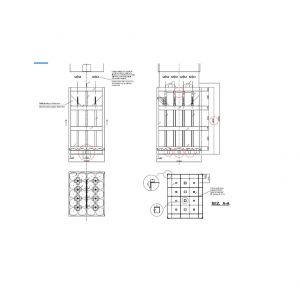
Main parts of the cylinder pack
Frame
The frame hold together the cylinders and the manifold. So it has give the stability for the complete construction. Must stand the double lifting weight. It has to keep the cylinders intact in case a harsh forklift handling. Must keep the pack parts together in case of accident when the bundle would fall down from the truck by a mistake or accident.
Regularly it is made from steel. And protected against corrosion. The most common industrial surface protection is the zinc plating (this could be hot deep zinc plating or thermal spraying). Surface protection also could be 1 component wet painting or 2 component wet painting or powder painting.
In case of offshore or marine usage where the corrosion resistance is more stricter against salt water then these technologies could be mixed as well for the longer life.
Connected to the frame I would mention two structural element:
- forklift pocket – has to give proper place where the gas battery could be manipulated with forklift without damaging it
- lifting eyes – in case of crane handling you have to have secure lifting eyes. It could be 1 central lifting eye or 2 lifting eyes or 4 lifting eyes. The 4 lifting eyes are more secure and stable solution. At the design and testing you have to check if the lifting with 2 hook is secure as well. Our actual maximum design weight is 1860 kg. In spite of this we use a 2 ton lifting eyes…and we use 4 pc from them. We prefer the lifting exes with screw fixture. In this case you can avoid the yearly inspection on the welded lifting point.
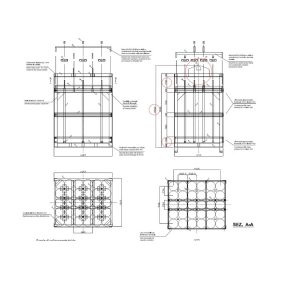
Dimensions of the gas bundle frame
The outer dimensions and the weight can be important because of 2 point:
- You have to be sure the bundles could be transport into the destination. If you have a small door with height of 2 meter then you cannot have a 2,05 meter bundle. So make always sure if your bundle outer dimensions are suit to the entrances and narrow spaces as well. Sometimes the bundles build from 120 liter 150 liter cylinders are higher then the 50 liter versions. In the Pwent Ltd we build bundles even from 20 liter or 15 liter cylinders as well. But this is an extreme situation. The width and depth is important on the transport truck or in the container as well. You have to keep in mind the optimal filling layout on those.
- The weight is an issue on a truck. How many bundles could you load on a full truck? If the bundle is lighter itself then you have more “space” for the gas.
Manifold
The manifold role is to connect together the pressure holding parts in a gas battery. It transfers the gas from the cylinders or to the cylinders through the fitting and through the main valve. Regularly the manifold has brass or stainless steel. The material compatibility for the gas is regulated by the ISO 11114 standard. Brass or copper material cannot use with aggressive gases and several other gases like the Ammonia or Cyonogen, Hydrogen or Dinitrogen oxid (N2O).
The stainless steel tubing do not have limitation. At brass the bending the processing is easier, the raw material is cheaper. The lifretime of the stainless steel manifold is longer. It could be used with all gases. The bending and forming is harder. You have to keep in mind several factor to choose the correct stainless steel material. For example the hydrogen has a rigidity factor against the metals. The 1.43 (or 304) is not good for hydrogen. 1.44 stainless steel material could stand against the hydrogen damaging effect.
Because manifold is a pressure holder part of the bundle, that is why it is design to stand 1,5 times higher pressure during testing. Of course you can just fill and use on the normal working pressure.
At the Pwent Ltd we are producing manifolds from stainless steels only for the high durability and long lifetime.
Double phase manifold
This is a special manifold layout. If you work with a liquified gas for example with CO2 bundle. If you would like to get liquid form of the gas and gas form from the bundle as well then you need a double phase manifold. This means in the cylinders there is a special adapter what give gas from the upper part of the cylinder. Beside this openings there is a diptube attached to the connector what could reach the liquide side of the cylinder content. Of course double phase means double tubing and double main outlet as well.
Main valve
From the viewpoint of the gas battery the main valve is the gate to the outer world. You have to always keep in minde 2 paramter for this:
- The outlet connection form has to suit to the pressure and type of the gas. It could be regulated country by country but the well known standards in Europe are: DIN477, BS341, AFNOR
- The orifice size is the second issue. The quantity of gas what could come through on the valve is very important. The orifice size of the main valve will determine the quantity of the gas what you can take from the bundle in a definite time. The bigger is better. The flow can be express is Cv (flow coefficient in US) or Kv (flow factor in Metric). This is a relative measure which show the quantity of flow through your valve.
You can have more main valve on a bundle. For example in our design you can have max 8 main valve on a 16x bundle. We created special bundle to an industrial diving company where we created 4 section with 2 valves on each section. This make possible to the company to have 4 divers parallel in work and has the possibility to top-fill the bundle if necessary during work.
Cylinders
The cylinders pressure and the certification has to be in line with the complete bundle pressure. Beside this the big portion of the bundle’s weight is arriving from the cylinder’s weight. For example a 50 liter 200 bar working pressure gas cylinder from Worthington is around 42 kg. The same from a less developed producer can be over 50-55 kg. If you multiply this weight difference by 12 or by 16 then the weight could be differ over 100 kg.
The cylinders could be positioned vertically (the cylinders are standing) or horizontally (the cylinders are laying).
Valves on the cylinders
In some case you would like to separate some of the gas. You would like to switch out some cylinder from the complete bundle. If you have on/off valve on each cylinder then you can do it easily. This make the cost of the bundle higher. In some cases – for example liquified gases – it is forbidden to use any closing valve within the manifold.
Pressure regulator
Nowadays the 200 bar and 300 bar or higher working pressure gas cylinder bundles are common. They are on the market together. They are available at the gas factories. The applications sometimes are designed to take 200 bar or 60 bar pressure from a gas source. If you have a 300 bar bundles in this case then you have to use a pressure regulator between the application and the source. Some bundles offer a integrated reduced pressure port beside the simple ports. You can have a pressure regulated port with 60 bar or 100 bar or 200 bar on a 300 bar working pressure bundle.
Standard of the gas cylinder bundle
The main standard for design a gas cylinder bundle is ISO 10961. It contains all information and rules for design, manufacture and test.
Marine/offshore bundles
We will explain more in a separate article the marine bundles. As a draft the marine bundles has to bear more effect from the elements. The surface protection has to be more thoughted on the cylinder and on the frame as well. The tilting angle what they have to stand without fall on the side has to be bigger. This comes from the instability on a ship board. The cylinders form the beginning – at the factory – has to be approved for marine use.
Signs on the gas bundle
You have to be able to identify always the gas cylinder bundle. The size of the battery make us able to use a data plate. This is obligatory. The data plate has to be resistance for the weather conditions. Regularly it is engraved on stainless metal plate. It contains the major data for the producer for the product and approvals. It contains the necessary retesting data as well. I give here 2 example for a TPED and for a PED data plate as well.
Colour coding of the gas cylinder bundle
The data plate identify everything. So the colour coding is not used on this area.
Colour coding of the gas cylinders in a gas cylinder bundle
The single cylinder colour coding is not obligatory in a gas cylinder bundle. The cylinders could be grey. It is written in the 6.2.2 point of the ISO 10961 standard.
Maintenance
In general according to the European rules the bundles for most common gases has to check every 10 year. In this test after dismounting and visual inspection the cylinders itself will be tested and the manifold separately will be tested as well.
Certification of gas cylinder bundles
PED (Pressure equipment directive) gas bundles
These type of gas packs can be used stationary. You cannot transport or move them under pressure. A typical usage of these are buffer tanks beside high pressure compressor or generator. CNG gas station buffer or N2 generator buffer.
The PED gas pack has to be equipped with safety valve itself.
TPED (Transportable pressure equipment directive) gas bundles
This is more typical solution. You can transport freely the gas battery. The TPED bundle does not have a safety valve itself. The filling technology has to provide an overfilling protection.
What is the main difference between the PED and TPED gas bundle?
The main difference is in the initial approval process. The certification criteria in 95% similar in PED and TPED. From the different certificate it is come you will have a separate certification on each . There are small difference in the naming on the data plate. For example the working pressure sign on
- TPED – No safety valve – PED must have safety valve
Can I use TPED cylinder in a PED gas cylinder bundle?
Yes. Regularly on stock the traders keep a TPED approved gas cylinders. If you need a gas cylinder bundle then the PED allow you to build a TPED approved gas cylinder in a PED gas bundle.
What is the normal temperature to use a gas cylinder bundle?
Regularly the cylinders itself are designed for a use between -20..+50 Celsius. The bundle as a complete equipment is suit to this range as well. If you need a bundle for Northern Europe part where you can have -40 Celsius then you have to ask for it in advanced.
How should I choose gas bundle?
There are several question what you have to able to answer for the proper choice. These are the following
- Gas type to use for.
- Working pressure what you need
- Certification – TPED, PED?
- Capacity what you need in liter – how many cylinder in which size you need?
- Dimensions or weight limits : Do you have dimension restrictions? Weight restriction?
- General layout – do you need sections? Do you need more main valve?
- Accessories what you need – valves on the cylinders? Dip tube? Pressure regulator?…
- Special usage conditions: like marine, offshore, extreme cold…