- For secure high-pressure
- +36 62 999 051
- info@pwent.eu
Gas cylinder sizes
Last Updated on 3 years ago by Lajos SZABÓ
I am asked many times about the general/most common gas cylinder sizes. What is the generally accepted gas cylinder sizes on the market? We would like to help you in this short article. We collect separately the low pressure gas cylinder sizes and the high-pressure most common gas cylinder sizes.
Industrial, medical, food gas cylinder sizes
In this category we generally refer to the high-pressure gas cylinders. This type of gases are for example carbon dioxide (CO2, UN1013), argon (Ar, UN1006), nitrogen (N2, UN1066), oxygen (O2, UN1072). The gas pressure in this category is above 60 bar. When you get the capacity of these gas cylinders in common you regularly get 3 type of definition: liter, kilogram or cubic meter.
3 main gas cylinder types
- Permanent/ gaseous gases – under this section we refer to gases what remain in gas form under pressure. Typical examples are nitrogen, oxygen, argon
- Liquified gases – these gases change its state under pressure. From gas form it go into liquid form under pressure. Good example could be the carbon dioxide or the sulphur dioxide
- Dissolved gases – these type of gases for the safe storage and transportation are dissolved in a solvent. The most famous gas is acetylene what is mainly dissolved in acetone.
You can find very good and precise materials at the Air Liquide Gas Encyclopedia page.
Permanent gases – gas cylinder sizes
In this group regularly we specify the size of the cylinders in litres or with cubic meters.
- The “liter” means always the water capacity of the gas cylinders. So in a 50 liter gas cylinder you can fill minimum 50 liter water. Into the 1 liter cylinders of course 1 liter and so on…
- If the cubic meter is the reference this means we already started to calculate with the working pressure. If you say 10 m3 oxygen gas cylinder then we regularly think on a 50 liter 200 bar working pressure. You can calculate the gas cylinder’s capacity to multiply the gas cylinder water capacity with the working pressure. 50×200 = 10 000 liter. So 10 000 liter oxygen can be stored in the 10 m3 cylinder. If we divided this with 1000 to get the cubic meter data: 10 m3. Another examples are:
- 50 liter gas cylinder on 300 bar working pressure: 50*300 = 15000 liter 15000/1000=15 m3
- 40 liter gas cylinder on 200 bar working pressure 40*200 = 8000 liter 8000/1000 = 8 m3
As we fill the gas into the gas cylinder the pressure inside this is proportionally increasing.
(In this calculation above we don’t calculate with the compressibility of the gas and the temperature change. We won’t touch this now).
On the market the most common gas cylinder sizes:
- 1 liter
- 2 liter
- 5 liter
- 10 liter
- 12 liter (mainly scuba usage)
- 15 liter (mainly scuba usage)
- 20 liter
- 40 liter
- 50 liter
- 80 liter
- 100 liter
- 110 liter
- 120 liter
- 130 liter
- 140 liter
- 150 liter
- 160 liter
- 180 liter
- 200 liter
Beside these main sizes you can find of course different sizes in different producers’ product range. They are not in regular production mainly they were produced for project.
Liquified gases – gas cylinder sizes
Regularly we refer to the capacity of the liquified gas cylinder sizes in kilogram. In our actual example we will look through the common sizes of the carbon dioxide and the PB (propane butane) gas cylinders. At liquified gases the gas under pressure from gas state go into liquide state. Over the liquified gas there is a pressurized gas layer This gas layer under normal condition has a stable stable pressure. That is why the liquified gases cannot be filled based on pressure – like at the permanent gases.
One completely full gas cylinder pressure will be the same like the half full cylinder’s pressure. Here the main data will be the weight of the filled gas. We measure the filled weight of the gas. That is why we refer to the cylinder capacity in kilogram. We give the maximum fillable gas weight.
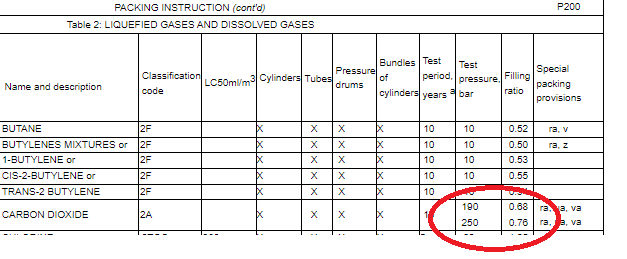
For the precise calculation we have to take a look into the ADR P200 table where we could define the maximum fillable gas quantitiy. For example as the table bellow show into a gas cylinder with 190 bar test pressure for every liter of the gas cylinder you cann fill 0,68 kg CO2. For example into a 50 liter gas cylinder you can fill 50 * 0,68 = 34 kg CO2 gas. Into a gas cylinder with 250 bar test pressure you can fill 0,76 kg gas into every liter of the cylinder. 50*0,76 = 38 kg. In the everyday life we calculate with x0,75 that is why the 50 liter gas cylinder could contains 37,5 kg CO2.
Carbon dioxide most common gas cylinder sizes
- 2 kg (2,67 liter)
- 4 kg (5,4 liter)
- 5 kg (6,7 liter)
- 6 kg (8 liter)
- 10 kg (13,4 liter)
- 20 kg (27 liter)
- 30 kg (40 liter)
- 37,5 kg (50 liter)
- 50 kg (67.7 liter)
- 60 kg (80 liter)
You can find our CO” cylinders here: CO2 gas cylinders from stock or from producer. Carbon dioxid filling (pwent.eu). If you cannot find suitable size please call us.
PB (propane butane) gas cylinder sizes
Here the question is that if you have a pure propane (C3H8, UN1978, 0,43 kg/liter 23 bar test pressure gas cylinder),or pure butane (C4H10, UN1011, 052 kg/liter 10 bar test pressure gas cylinder) or some mix of them in the cylinder. This could cause some variance in the filling ratio of weight/liter.
- 2 kg (4,8 liter)
- 6 kg (14,3 liter)
- 11 kg (26,2 liter)
- 13 kg (31 liter)
- 19 kg (38 liter)
- 47 kg (94 liter)
You can find our different gas cylinder sizes here: Különböző gázpalack típusainkat itt találja: