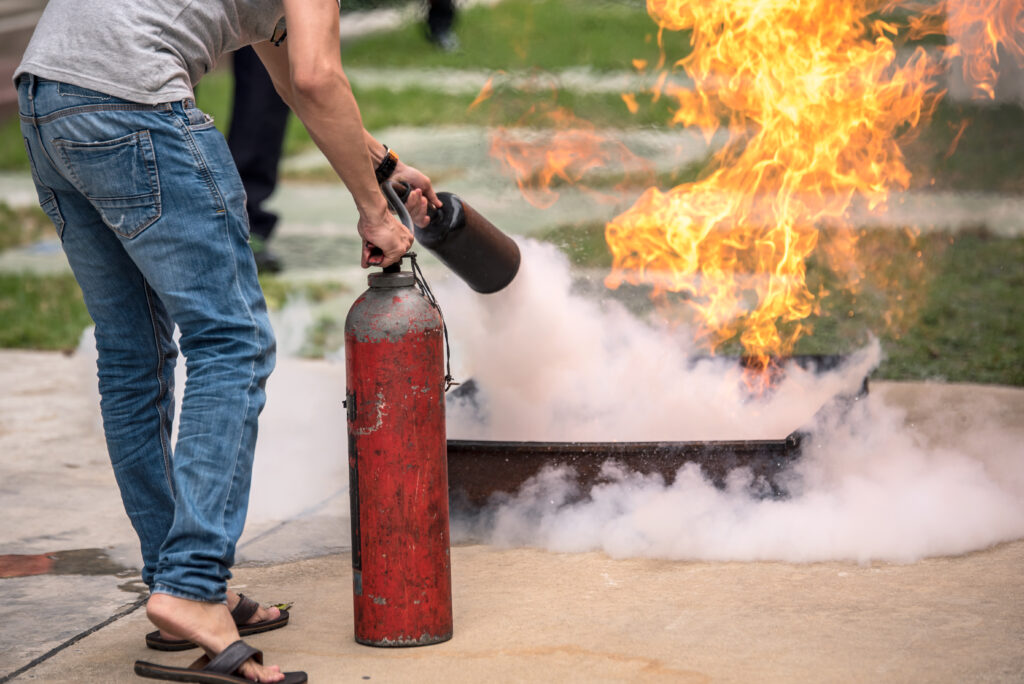- For secure high-pressure
- +36 62 999 051
- info@pwent.eu
Empowering Employees with Fire Safety Training
Last Updated on 2 years ago by admin
Ensuring the safety and well-being of employees is crucial in today’s fast-paced work environments. Among the various safety measures, fire safety training stands out as a cornerstone of workplace safety. By providing employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to prevent, identify, and respond to fire emergencies, organizations not only fulfill their legal obligations but also create a safer and more secure work environment for everyone involved. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the importance of fire safety training in the workplace, the specific benefits it offers to employees, and how organizations can effectively implement and conduct such training sessions.
Benefits of Fire Safety Training for Employees
Organizations can significantly reduce the risk of fire incidents by educating employees about fire hazards, prevention techniques, and emergency response procedures.
Protecting Life and Property
One of the most significant benefits of fire safety training is its role in safeguarding both lives and property.
Trained employees are better equipped to identify potential fire hazards in the workplace, such as faulty electrical wiring, flammable materials, or improperly stored chemicals, and take proactive measures to mitigate these risks.
Moreover, in a fire emergency, trained employees can respond swiftly and effectively, helping to minimize property damage and, more importantly, ensuring the safety and well-being of their colleagues.
Boosting Employee Morale
In addition to protecting life and property, fire safety training is crucial in boosting employee morale and confidence. When employees receive comprehensive training on fire safety protocols and procedures, they gain a greater sense of security and empowerment in their workplace.
Knowing that they are equipped with the knowledge and skills to handle fire emergencies effectively, employees feel more confident in their ability to respond to challenging situations. This increased confidence enhances overall morale and fosters a culture of safety and accountability within the organization, where employees actively look out for one another’s well-being.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with fire safety regulations is an organization’s legal and moral obligation. Fire safety training helps employees understand and adhere to these regulations, reducing the risk of regulatory violations and associated penalties.
Organizations can demonstrate their commitment to upholding the highest safety and compliance standards by providing regular training sessions on fire safety protocols. Moreover, staying abreast of evolving regulations and industry best practices ensures that employees are adequately prepared to navigate the ever-changing landscape of fire safety requirements.
Improving Reputation and Public Relations
Organizations prioritizing fire safety training demonstrate their commitment to the well-being of their employees and stakeholders, which can positively impact their reputation and public relations.
By proactively investing in employee safety and training initiatives, organizations signal to clients, partners, and the broader community that they prioritize safety above all else. This proactive approach enhances the organization’s reputation and builds stakeholder trust and confidence. In a fire incident, having well-trained employees who can respond effectively can further bolster the organization’s reputation and demonstrate its commitment to safety and preparedness.
What is Covered in Fire Safety Training?
Fire safety training encompasses various topics and practical skills designed to equip employees with the knowledge and tools to effectively prevent, identify, and respond to fire emergencies. Below, we look at some key areas covered in fire safety training.
Identifying potential fire hazards:
Training individuals to recognize common fire hazards in the workplace, such as electrical faults, combustible materials, and flammable liquids. This includes understanding the concept of the fire triangle—oxygen, heat, and fuel—and how various factors can contribute to fire risk.
Safe practices to prevent fires:
Educating employees on best practices for fire prevention, including proper storage and handling of flammable materials, regular maintenance of electrical equipment, and adherence to smoking policies and fire safety protocols.
Emergency response procedures:
Providing employees with clear and actionable guidance on responding to fire emergencies, including procedures for raising the alarm, evacuating the building safely, and contacting emergency services. This may involve conducting drills and simulations to practice evacuation procedures and familiarize employees with emergency exits and assembly points.
Proper use of fire extinguishers:
Training employees on the different fire extinguishers available, their respective uses and limitations, and proper techniques for deploying them effectively. This includes hands-on practice with fire extinguisher simulators to ensure employees are comfortable and competent using this critical firefighting equipment.
Organized evacuations
Establishing clear evacuation routes and assembly points and educating employees on the importance of evicting the building safely and efficiently during a fire emergency. This may involve assigning designated evacuation wardens or marshals to coordinate evacuation efforts and ensure all employees are accounted for.
EU Standards for Fire Safety Training
In the European Union, building fire safety is governed by comprehensive regulations and standards to protect occupants and property from fire risk. These regulations outline specific requirements for fire safety training, emergency preparedness, and building design and construction to minimize the likelihood of fire incidents and mitigate their potential impact. Key considerations for fire safety training in the EU include:
1. Prevention measures
Emphasizing the importance of fire prevention measures, such as regular maintenance of fire detection and suppression systems, proper storage of flammable materials, and adherence to smoking bans and other fire safety protocols.
2. Safe evacuation procedures
Establish clear evacuation routes and assembly points, conduct regular evacuation drills, and ensure all occupants are familiar with emergency procedures and protocols.
3. Proper use of firefighting equipment
Train occupants on using fire extinguishers, fire blankets, and other firefighting equipment, and ensure that such equipment is readily accessible and well-maintained.
4. Compliance with building codes and standards
Ensuring that buildings comply with relevant fire safety codes and standards, including requirements for fire resistance, compartmentalization, means of egress, and fire detection and suppression systems.
Summary
By providing employees with the knowledge and skills to prevent, identify, and respond to fire emergencies effectively, organizations can create a safer and more secure work environment for everyone involved. Moreover, by staying abreast of regulatory requirements and industry best practices, organizations can ensure compliance with relevant fire safety standards and demonstrate their commitment to upholding the highest standards of safety and preparedness.
Pwent provides innovative services for producing and servicing companies working for safe and efficient fire protection systems. The company specializes in the production of gas cylinder bundles, gas cylinders, machinery, and fire extinguisher testing and refurbishment and the handling of powder extinguishers, CO2 extinguishers, and chemical agents.